Paul Beaud et al.: A time-dependent order parameter for ultrafast photoinduced phase transitions
August 3, 2014Square dance of the atoms: Shedding light on ultrafast phase transitions
(From the PSI Synchrotron Radiation and Nanotechnology Scientific Highlights)The exploration of the interaction of structural and electronic degrees of freedom in strongly correlated electron systems on the femtosecond time scale is an emerging area of research. One goal of these studies is to advance our understanding of the underlying correlations, another to find ways to control the exciting properties of these materials on an ultrafast time scale. So far a general model is lacking that provides a quantitative description of the correlations between the structural and electronic degrees of freedom.
Strongly correlated electron systems often exhibit very strong interactions between structural and electronic degrees of freedom that lead to complex and interesting phase diagrams. For technological applications of these materials it is important to learn how to drive transitions from one phase to another. A key question here is the ultimate speed of such phase transitions, and to understand how a phase transition evolves in the time. Here Paul Beaud and his collegues apply time-resolved X-ray diffraction to directly measure the changes in long-range order during ultrafast melting of the charge and orbitally ordered phase in a perovskite manganite. They find that although the actual change in crystal symmetry associated with this transition occurs over different timescales characteristic of the many electronic and vibrational coordinates of the system, the dynamics of the phase transformation can be well described using a single time-dependent ‘order parameter’ that depends exclusively on the electronic excitation.
Beaud, P., Caviezel, A., Mariager, S.O., Rettig, L., Ingold, G., Dornes, C., Huang, S.W., Johnson, J.A., Radovic, M., Huber, T., Kubacka, T., Ferrer, A., Lemke, H.T., Chollet, M., Zhu, D., Glownia, J.M., Sikorski, M., Robert, A., Wadati, H., Nakamura, M., Kawasaki, M., Tokura, Y., Johnson, S.L., and Staub, U. (2014) A time-dependent order parameter for ultrafast photoinduced phase transitions. Nature Mater 13, 923-927 (10.1038/nmat4046)

Schematic set-up of the optical-pump/X-ray-probe experiment.
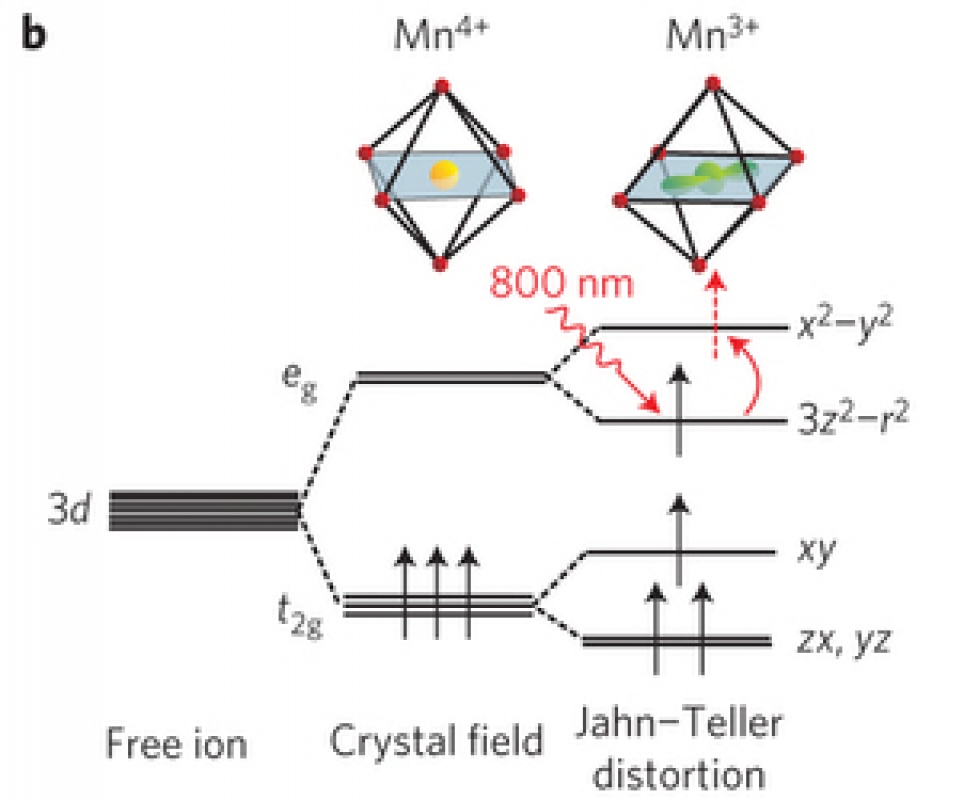
b In the cubic crystal field the degenerate Mn 3d states are split into the eg andtg bands. In the ground state, distortions of the oxygen octahedra at the Mn3+ sites further split the bands (Jahn–Teller effect).

c On cooling to the ground state charge and orbital order is observed alongside with a Jahn–Teller distortion of the Mn3+O6 octahedra, leading to a doubling of the unit cell along the b axis and a symmetry change from orthorhombic Pbnm to monoclinic P21/m
back <<

 Ursula Keller wins “Swiss Nobel” Marcel Benoist Prize
Ursula Keller wins “Swiss Nobel” Marcel Benoist Prize Farewell: the NCCR MUST ended
Farewell: the NCCR MUST ended  MUST2022 Conference
MUST2022 Conference New scientific highlights
New scientific highlights FELs of Europe prize for Jeremy Rouxel
FELs of Europe prize for Jeremy Rouxel Ruth Signorell wins Doron prize
Ruth Signorell wins Doron prize New FAST-Fellow Uwe Thumm at ETH
New FAST-Fellow Uwe Thumm at ETH International Day of Women and Girls in Science
International Day of Women and Girls in Science New scientific highlight
New scientific highlight EU XFEL Young Scientist Award for Camila Bacellar,
EU XFEL Young Scientist Award for Camila Bacellar, Prizes for Giulia Mancini and Rebeca Gomez Castillo
Prizes for Giulia Mancini and Rebeca Gomez Castillo Nobel Prize in Chemistry awarded to RESOLV Member Benjamin List
Nobel Prize in Chemistry awarded to RESOLV Member Benjamin List Hans Jakob Wörner invited to give the „New Horizons Solvay Lectures”
Hans Jakob Wörner invited to give the „New Horizons Solvay Lectures”  Unusual keynote talk at an international scientific conference
Unusual keynote talk at an international scientific conference NCCR MUST at Scientifica 2021
NCCR MUST at Scientifica 2021