Anisotropic photoemission time delays close to a Fano resonance
March 6, 2018Atomic time delay evolution across an autoionizing state
Attosecond photo ionziation delays have been first measured in the multi-photon / strong field regime in 2008, referred to as the tunnel ionization 1 and then in 2010 the single-photon regime, referred to as the photoemission2. Since then it has become a very active field of reseach in attosecond science with intense theoretical debates in both cases.
In the simplest case, when the electron is promoted into a flat (non-resonant) continuum by direct laser-assisted photoionization, the measured delay after absorbing a single XUV photon is related to the group delay of the departing electron wave packet induced by the ionic potential and laser field, respectively 3. This delay is also referred to as the Wigner delay.
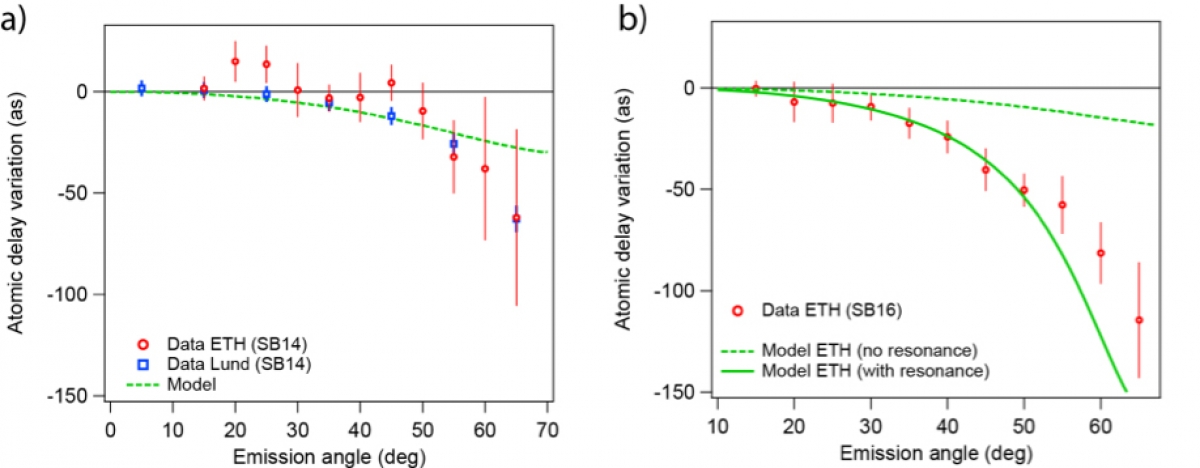
The situation becomes more complicated when ionization occurs in the vicinity of autoionizing states which distort the phase of the emitted photoelectron wavepacket 4. A benchmark study performed with helium 5 showed that in non-resonant conditions the photoemission time delay has no angular dependence. In this work, we demonstrate how the angular dependence of the atomic time delays is also strongly affected by correlation effects associated to the mechanism of autoionization, thus giving access to angle-resolved multi-electron dynamics on the attosecond time scale. The presence of autoionizing states clearly manifests in the measured time delays for both the narrow 3s-15p and the broad 3s-14p resonances. They are also very visible in the anisotropy parameters extracted from time-integrated photoelectron angular distributions (PADs) generated by two-photon absorption.
These results demonstrate that not only the phase of the photoelectron wave packet is significantly distorted in the presence of resonances, but that this distortion depends on the electron emission angle. The effect of the resonance on the angular dependence of the atomic delay is due to the existence of several open channels with different angular emission properties and with a varying amplitude across the resonance.
1. P. Eckle, A. N. Pfeiffer, C. Cirelli, A. Staudte, R. Dörner, H. G. Muller, M. Büttiker, and U. Keller, "Attosecond ionization and tunneling delay time measurements in helium," Science 322 (5907), 1525-1529 (2008).
2. M. Schultze, M. Fiess, N. Karpowicz, J. Gagnon, M. Korbman, M. Hofstetter, S. Neppl, A. L. Cavalieri, Y. Komninos, T. Mercouris, C. A. Nicolaides, R. Pazourek, S. Nagele, J. Feist, J. Burgdorfer, A. M. Azzeer, R. Ernstorfer, R. Kienberger, U. Kleineberg, E. Goulielmakis, F. Krausz, and V. S. Yakovlev, "Delay in Photoemission," Science 328 (5986), 1658-1662 (2010).
3. J. M. Dahlström, A. L'Huillier, and A. Maquet, "Introduction to attosecond delays in photoionization," Journal of Physics B: Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics 45, 183001 (2012).
4. M. Sabbar, S. Heuser, R. Boge, M. Lucchini, T. Carette, E. Lindroth, L. Gallmann, C. Cirelli, U. Keller, “Resonance effects in photoemission time delays,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 133001, 2015.
5. S. Heuser, Á. Jiménez-Galán, C. Cirelli, C. Marante, M. Sabbar, R. Boge, M. Lucchini, L. Gallmann, I. Ivanov, A. S. Kheifets, J. M. Dahlström, E. Lindroth, L. Argenti, F. Martín and U. Keller, “Angular dependence of photoemission time delay in helium,” Phys. Rev. A, vol. 94, 063409, 2016.
Highlight reference: Cirelli, C., C. Marante, S. Heuser, C. L. M. Petersson, Á. J. Galán, L. Argenti, S. Zhong, D. Busto, M. Isinger, S. Nandi, S. Maclot, L. Rading, P. Johnsson, M. Gisselbrecht, M. Lucchini, L. Gallmann, J. M. Dahlström, E. Lindroth, A. L’Huillier, F. Martín and U. Keller (2018). Anisotropic photoemission time delays close to a Fano resonance. Nat. Commun. 9: 955. (10.1038/s41467-018-03009-1)
 Cirelli-2018.
Cirelli-2018.<<

 Ursula Keller wins “Swiss Nobel” Marcel Benoist Prize
Ursula Keller wins “Swiss Nobel” Marcel Benoist Prize Farewell: the NCCR MUST ended
Farewell: the NCCR MUST ended  MUST2022 Conference
MUST2022 Conference New scientific highlights
New scientific highlights FELs of Europe prize for Jeremy Rouxel
FELs of Europe prize for Jeremy Rouxel Ruth Signorell wins Doron prize
Ruth Signorell wins Doron prize New FAST-Fellow Uwe Thumm at ETH
New FAST-Fellow Uwe Thumm at ETH International Day of Women and Girls in Science
International Day of Women and Girls in Science New scientific highlight
New scientific highlight EU XFEL Young Scientist Award for Camila Bacellar,
EU XFEL Young Scientist Award for Camila Bacellar, Prizes for Giulia Mancini and Rebeca Gomez Castillo
Prizes for Giulia Mancini and Rebeca Gomez Castillo Nobel Prize in Chemistry awarded to RESOLV Member Benjamin List
Nobel Prize in Chemistry awarded to RESOLV Member Benjamin List Hans Jakob Wörner invited to give the „New Horizons Solvay Lectures”
Hans Jakob Wörner invited to give the „New Horizons Solvay Lectures”  Unusual keynote talk at an international scientific conference
Unusual keynote talk at an international scientific conference NCCR MUST at Scientifica 2021
NCCR MUST at Scientifica 2021